Electricity
Of primary origin (hydraulic, nuclear or other renewables) or secondary (thermal biomass, coal, fuel oil or natural gas), electricity is the emblematic energy vector of modernity. This is evidenced by the enormous differences in consumption between an American and a Sahelian. The ability to pursue its development, production, transport and distribution, while respecting the environment, is now at the heart of the global energy issue.
10 March 2023
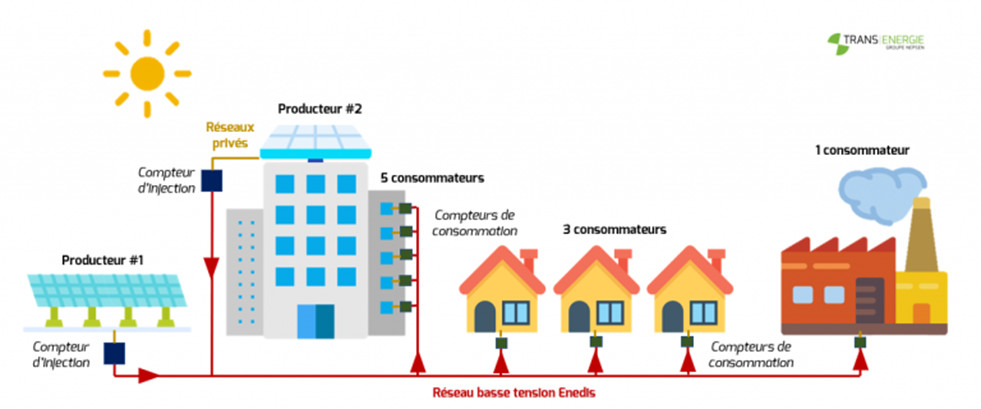
1. Historical, technical and legal context of collective self-consumption Individual and collective self-consumption is historically the origin of energy consumption where populations used the energy they were able to collect themselves. This notion reappeared when the decentralization of the networks was developed again. 1.1) History and position in the development
- DEMARS Pierre-Thomas
- Niveau de lecture
12 October 2022
Incidents on electricity grids due to the presence of growing wind and solar PV capacities with intermittent production tend to recur in Europe, as in other regions of the world. Variable input renewable energies (VRE), pose two main security of supply problems for electrical systems. The first is the variability
 Dominique Finon
Dominique Finon- Niveau de lecture
27 July 2021
The liberalization reforms of the electricity sector in the 1990s introduced an institutional regime in which equipment decisions and investment risk management are privatized and decentralized among competing agents (See: Les marchés électriques : complexité et limites de la libéralisation des industries électriques). This role used to be based on
 Dominique Finon
Dominique Finon- Niveau de lecture
8 June 2021
The notions of energy communities are very disparate. There are communities that originate from local initiatives and physically occupy a small piece of territory, neighbourhood, village, or campus. This is the type of community referred to below. But there are also other communities of the virtual type, with geographically dispersed
 WILD Jean
WILD Jean- Niveau de lecture
8 June 2021
&nbp; The development of electricity production in the last decades of the 19th century was based on the creation of a market, which implied that, in order to be sold, electricity had to be metered. This led to the development of the first electromagnetic meters (Figure 1), following the
 WILD Jean
WILD Jean- Niveau de lecture
19 April 2021
The focus of low-carbon transition policies on intermittent renewable energies (RE) in the electricity sector leads to the search for economic means to cope with the variability of these productions and to give a value to the surplus of RE electricity production compared to the hourly demand in systems where
 Dominique Finon
Dominique Finon- Niveau de lecture
10 December 2020
In developed countries engaged in renewable energy-based decarbonation policies, electricity storage is one of the priorities for action. This is the case in Germany with its Energiewende policy, which aims to develop up to 80% of renewable energy in the electricity sector by 2050, in particular by subsidising batteries associated
- Niveau de lecture
23 May 2018
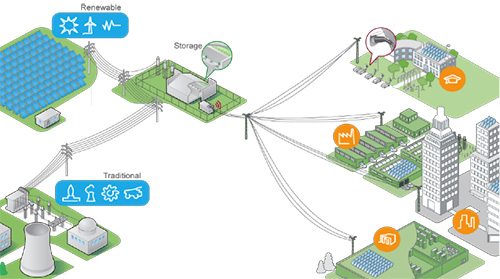
Microgrids enable an optimized way to access reliable, green, and resilient energy through a local, interconnected energy system within clearly defined electrical boundaries, which incorporate loads, decentralized energy resources, battery storage, and control capabilities. Let’s see in more detail what a microgrid is and what benefits it delivers. 1. What
 BOUTIN Véronique
BOUTIN Véronique- Niveau de lecture
22 February 2016
In a power system with increased need for flexibility, wind and solar power are characterised by considerable volatility across different scales and their output cannot be predicted with certainty. In order to deal with the resulting variations and forecast errors, system operators as well as electricity markets will need to
- WEISROCK Ghislain
- Niveau de lecture